| Version 17 (modified by , 5 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
Graphical Login (VNC) ... manual connection
Using VNC requires three general steps.
- Prepare your account on a JURECAVIS node.
- Start a VNC server on a JURECA node.
- Tunnel VNC traffic to your workstation.
- Start a VNC viewer on your workstation and connect to the VNC server.
1. Prepare your account …
Before you use VNC for the first time you have to prepare your account:
- login to a JURECAVIS node
- create the directory ~/.vnc
- define VNC password
ssh <USERID>@jurecavis.fz-juelich.de mkdir ~/.vnc vncpasswd
2. Start VNC server …
The following steps are necessary to start a VNC server on JURECA.
Please notice that you have two general options:
You can start the VNC server ...
- on an interactive vis login node
- + no batch system == instant access
- -- system is shared with other users
- on a dedicated vis node
- + system is not shared (exclusive use)
- -- access through batch system
In case the VNC server could successfully be started (details in 2a,b), you will find a simular line in the output:
Desktop 'TurboVNC: jurecavis02.fz-juelich.de:1 (profile <PROFILE>)' started on display jrc1384:1 (jurecavis02.fz-juelich.de:1)
Two important informations have to be taken from this output
to setup the required SSH tunnel (with the correct network port) to the allocated node in step 2:
- The allocated node is jurecavis02
- The number of the VNC display is :1
It is very important to know that the network port of the VNC server depends on this display number.
The actual port number is 5900+<VNC display>, therefore port 5901 must be tunneled in this case.
Important notes:
- To ensure VNC sessions are not forgotten and keep on running forever, they will be killed after 24 hours (WITHOUT warning).
- Logout from your VNC session, after you have finished your work. This will save resources and close the VNC server.
- If you start the VNC server the first time, you will be asked for a password (which is stored in ~/.vnc/passwd).
You will be asked for this password by the VNC viewer, when you connect to the VNC server.
To reset the password just delete the file ~/.vnc/passwd.
a. ... on an interactive vis login node
Open a SSH shell on an interactive vis login node (jurecavis.fz-juelich.de):
ssh <USERID>@jurecavis.fz-juelich.de
Start your own VNC server on jurecavis. Usefull vncserver parameters are:
- -profile -> choose a profile (eg. -profile vis)
- -geometry -> set the screen size (eg. -geometry 1920x1080)
# start the VNC server on visualization login node vncserver -profile vis -geometry 1920x1080 -fg ... Desktop 'TurboVNC: <NODE>:<DISPLAY> (profile <PROFILE>)' started on display <NODE>:<DISPLAY> (<NODE>:<DISPLAY>) ...
b. ... on a dedicated vis node
Open an SSH shell on any login node of JURECA the usual way:
ssh <USERID>@jureca.fz-juelich.de
sbatch is used to start a job script. In this case the job script should start the vnc server and could look like:
#!/bin/bash #SBATCH --job-name=vnc #SBATCH --nodes=1 #SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=28 #SBATCH --gres=gpu:2 #SBATCH --partition=vis #SBATCH --time=24:00:00 #SBATCH --mem=512000 vncserver -fg -profile vis -geometry 1920x1080
Once you have created this job script, you can start it by
sbatch -A <computebudget> <NAME_OF_JOBSCRIPT>
The option '--start-xserver' tells sbatch that it should start an X-server on the allocated node, which is important if you want to do hardware rendering on a GPU.
Once the job ist started, you have to find out the name of the node on which the job is running and the number of the vnc display.
To do this you have to look at the output file generated by slurm, e.g.:
cat slurm-2063855.out Desktop 'TurboVNC: jrc1386:2 (profile vis)' started on display jrc1386:2 (jrc1386:2) Starting applications specified in /etc/turbovnc/xstartup.turbovnc Log file is /homeb/.../your_user_name/.vnc/jrc1386:2.log
In this case the node is jrc1386 and the display number is 2. This information is needed to set up the ssh tunnel (see step 3).
3. Tunnel VNC traffic to workstation
Now you have to open an SSH tunnel from your workstation to node on which your VNC server is running.
The steps to be done depend strongly on your operating system and your setup.
Linux:
If your operating system is Linux use for interactive nodes (NODE is most likely jurecavis01... or jurecavis02...):
and for dedicated nodes:
Windows:
In case your operating system is Windows, the setup of the tunnel depends on your ssh client.
Here a short overview on how-to setup a tunnel with PuTTY is given.
It is assumed that PuTTY is already configured in a way that a general ssh connection to JURECA is possible.
That means that host name, user name and the private ssh key (using PuTTY's Pageant) are correctly set.
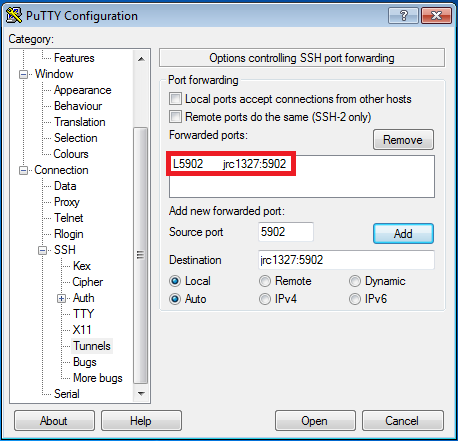
To establish the ssh tunnel, enter the "SSH-->tunnels" tab in the PuTTY configuration window.
You have to enter the source port (eg. <5900+DISPLAY> = 5902 if DISPLAY=2) and the destination (in this case localhost:<5900+DISPLAY>) and than press add.
After pressing add, the tunnel should appear in the list of forwarded ports and you can establish the tunnel by pressing the open button:
4. Start a VNC viewer and connect
|
|---|
If you are using Linux, a VNC viewer typically is already part of the distribution or can be installed from a repository.
For Windows, a VNC viewer can be downloaded for example here.
Start your local VNC client and connect to localhost:<DISPLAY>, e.g.:
After typing in your VNC password (defined in step 1), you will have access to the remote graphical desktop running on the visualization node of JURECA.
any feedback welcomed - h.zilken@…, j.goebbert@…
Attachments (4)
- PuTTY-add-tunnel.png (23.5 KB ) - added by 8 years ago.
- PuTTY-tunnel-added.png (26.2 KB ) - added by 8 years ago.
- Trac_Setup_VNC.png (105.3 KB ) - added by 8 years ago.
- turbovnc-128.png (7.1 KB ) - added by 6 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip