| Version 1 (modified by , 8 years ago) ( diff ) |
|---|
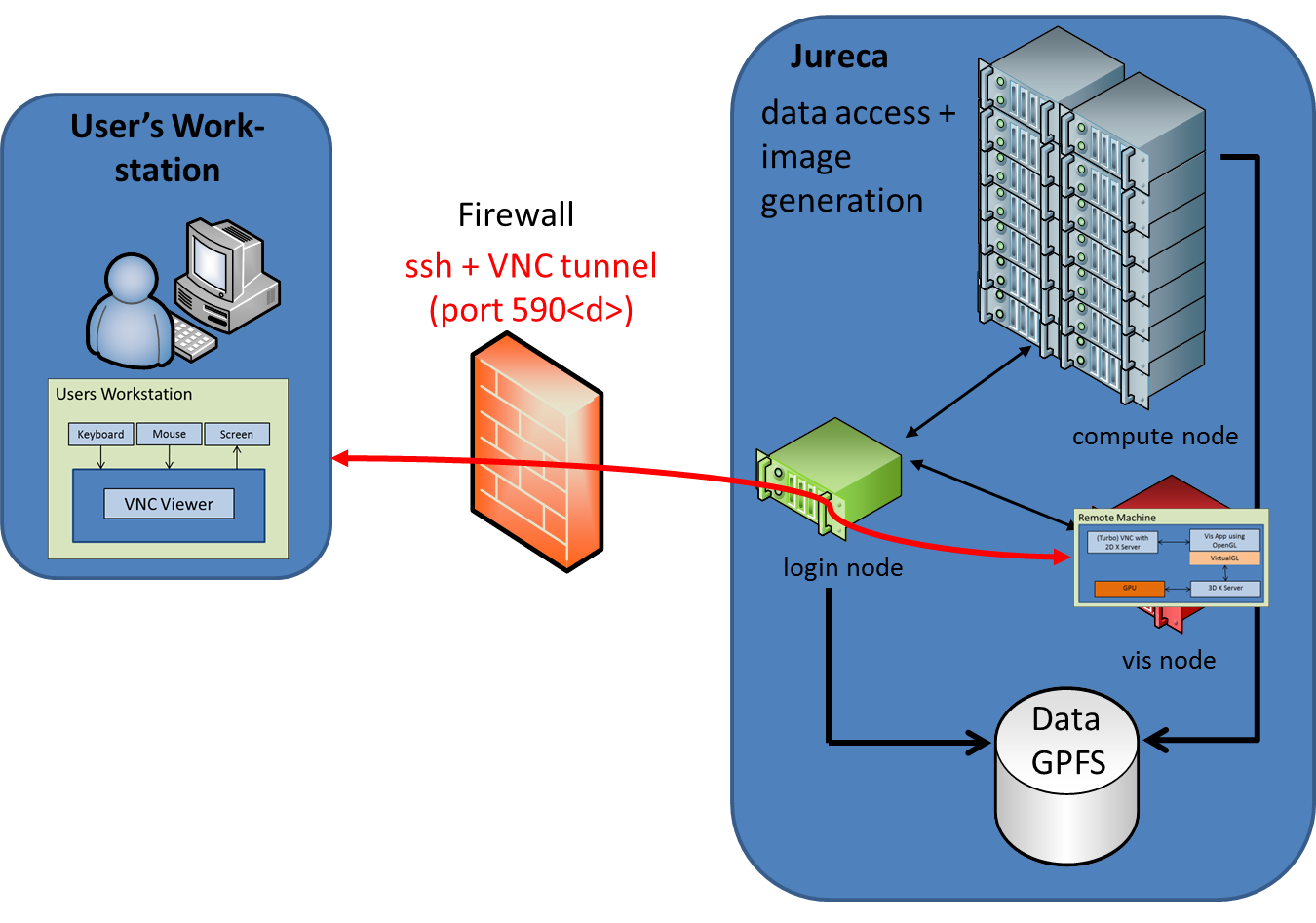
VNC - more details
VNC follows a very general approach, where a remote graphical desktop on one node of the remote cluster is started.
On the user's workstation only a lightweight VNC viewer has to be installed.
The graphical screen of the remote desktop is send as an image from the cluster to the viewer on the fly.
The user can work with this remote graphical desktop in the usual way, just by interacting with keyboard and mouse.
This is a very convenient way to work on a remote machine, not only for data visualization.
VNC offers the ability to detach from a session (running in a VNC server) and then attach back at a later time.
That means, that the user can close the VNC viewer on his/her computer and any application started in the VNC session on the server keeps on running - they do not pause or even be killed.
Later on the user can connect back to the same VNC session (even from a different computer) and keep on working.
hardware accelerated rendering (OpenGL)
 Whenever an OpenGL capable visualization software, like VisIt, is started on the remote cluster node,
Whenever an OpenGL capable visualization software, like VisIt, is started on the remote cluster node,
OpenGL commands can be redirected to the GPU of this node with the help of VirtualGL.
- ... using vglrun (e.g. vglrun paraview)
This way the hardware accelerated rendering capabilities of a cluster node (if available) can be exploit for remote rendering.
(attention: without VirtualGL software, rendering using the CPU instead of the GPU must be used (if available), which is much slower).
Attachments (1)
- Trac_Setup_VNC.png (211.9 KB ) - added by 8 years ago.
Download all attachments as: .zip